Downregulation of microRNA-34 induces cell proliferation and
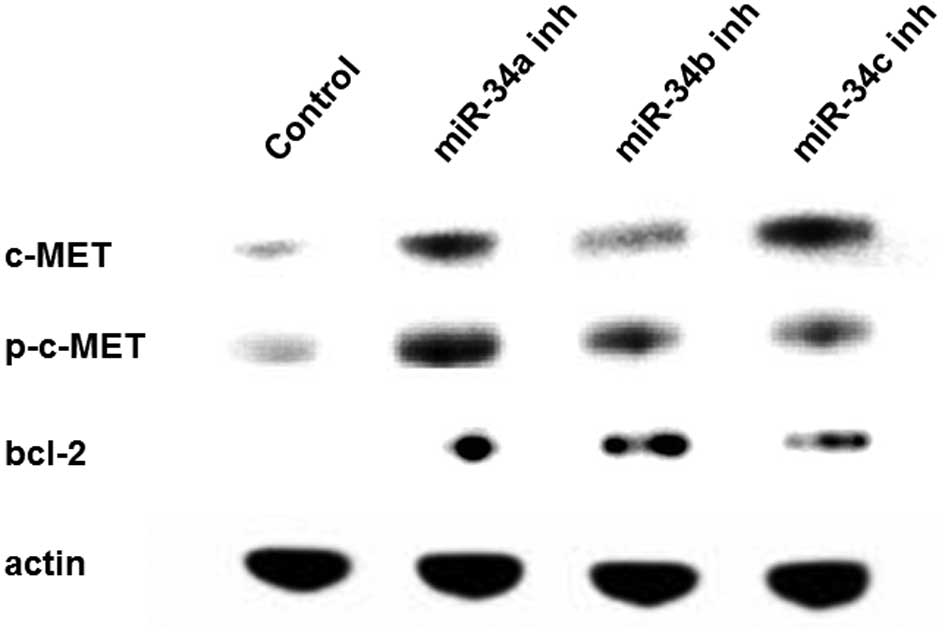
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is an aggressive tumor with a dismal prognosis, and the molecular alterations involved in this disease remain unknown. We previously reported that microRNA-34s (miR-34s) are methylated and downregulated in MM and may play an important role in the carcinogenesis of MM. In this study, we downregulated miR-34s in human mesothelial cells to investigate the cellular effect of miR-34 knockdown. For the cell study, we used LP-9, a human mesothelial cell line, and three human primary-cultured mesothelial cell lines. RNA-based miR-34a, -34b and -34c inhibitors were transfected into these cells, and their effects on proliferation and invasion were evaluated. A scramble RNA oligonucleotide was used as a control. The protein expression status was estimated using western blotting. After miR-34 inhibitor transfection, miR-34a, -34b and -34c were downregulated in all the examined mesothelial cell lines. miR-34 inhibitor transfection significantly increased cell proliferation in all of the mesothelial cell lines, compared with the scramble control. The invasive ability also increased in the miR-34 inhibitor transfectants, compared with the scramble control, in the LP-9 cell line. Western blotting confirmed the upregulation of c-MET, phospho-c-MET, and bcl-2 proteins in LP-9 cells after miR-34 inhibitor transfection. In conclusion, our study showed that the downregulation of miR-34s induced an oncogenic phenotype in non-malignant mesothelial cells. The present study, together with the results of our previous report, strongly suggest that miR-34s play an important role in the early carcinogenic process involved in the transformation of human mesothelial cells to MM.

MicroRNA-34a: the bad guy in age-related vascular diseases

Role of Stromal Fibroblast–Induced WNT7A Associated with Cancer Cell Migration Through the AKT/CLDN1 Signaling Axis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma - Laboratory Investigation

MicroRNA: a novel implication for damage and protection against ionizing radiation

Deciphering signaling pathway interplay via miRNAs in malignant pleural mesothelioma - ScienceDirect

MicroRNA-34a: the bad guy in age-related vascular diseases

Journal of Cellular Physiology, Cell Biology Journal

Full article: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 gene (PVT1) modulates the proliferation and apoptosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells by sponging miR-486-5p
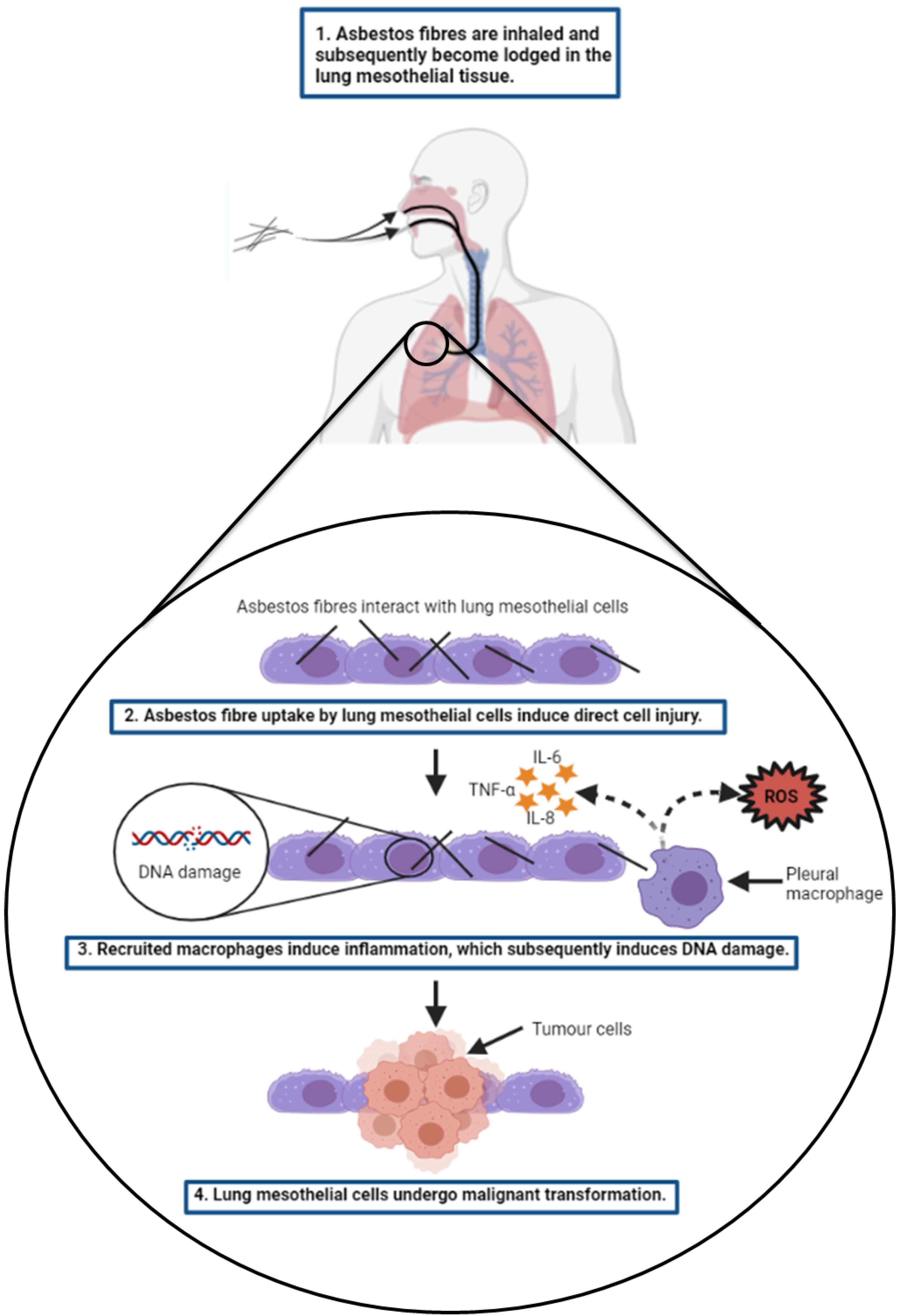
Onco, Free Full-Text

Melodic maestros: Unraveling the role of miRNAs in the diagnosis, progression, and drug resistance of malignant pleural mesothelioma - ScienceDirect
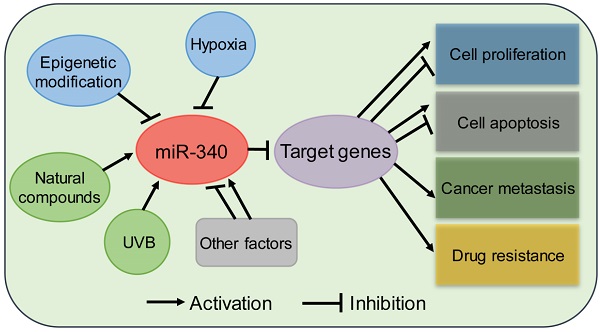
miR-340: A multifunctional role in human malignant diseases

Interplay of non-coding RNAs and approved antimetabolites such as gemcitabine and pemetrexed in mesothelioma - ScienceDirect
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Alternative mechanisms of miR-34a regulation in cancer







