Finite element analysis of compression fractures at the
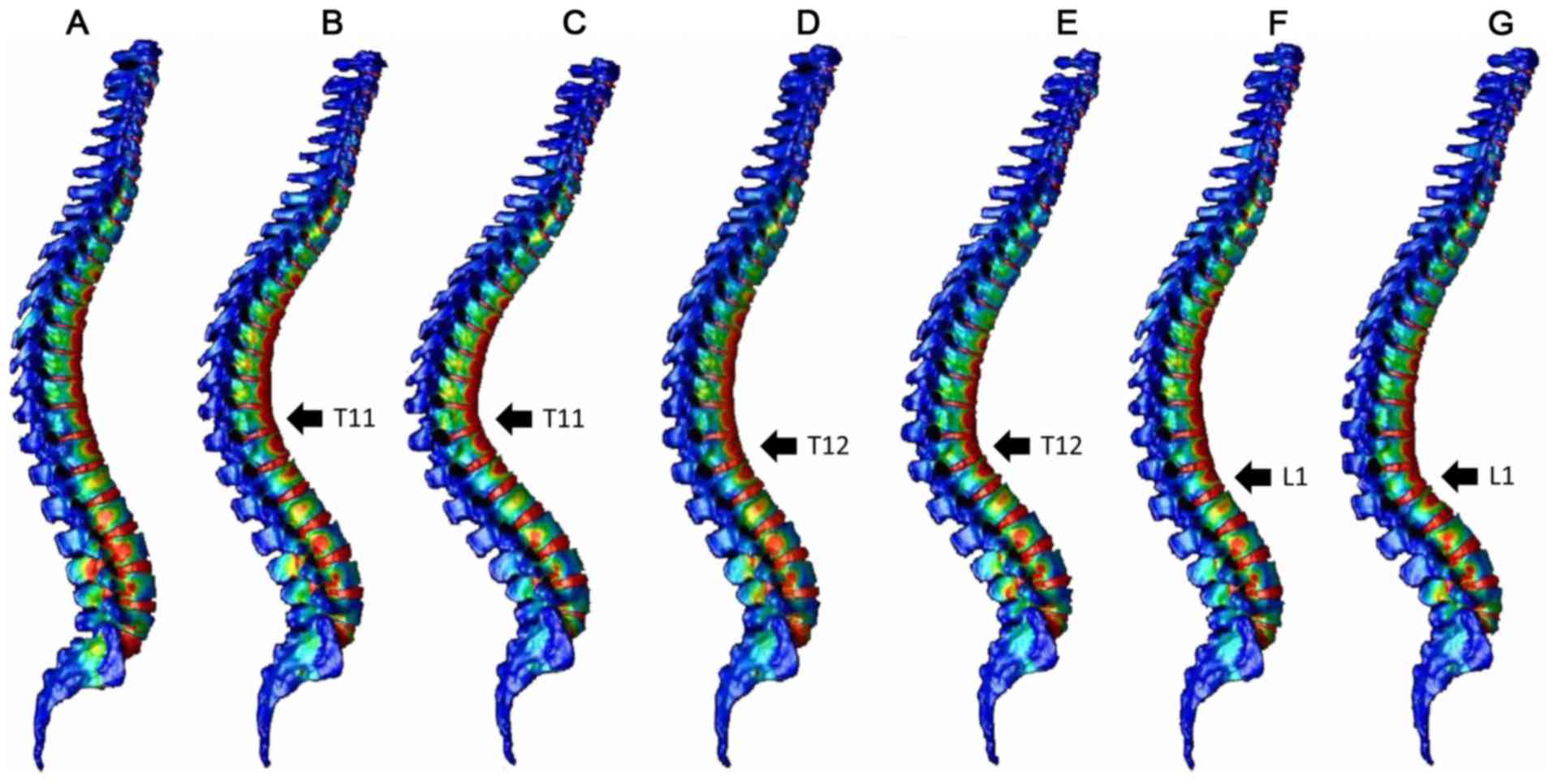
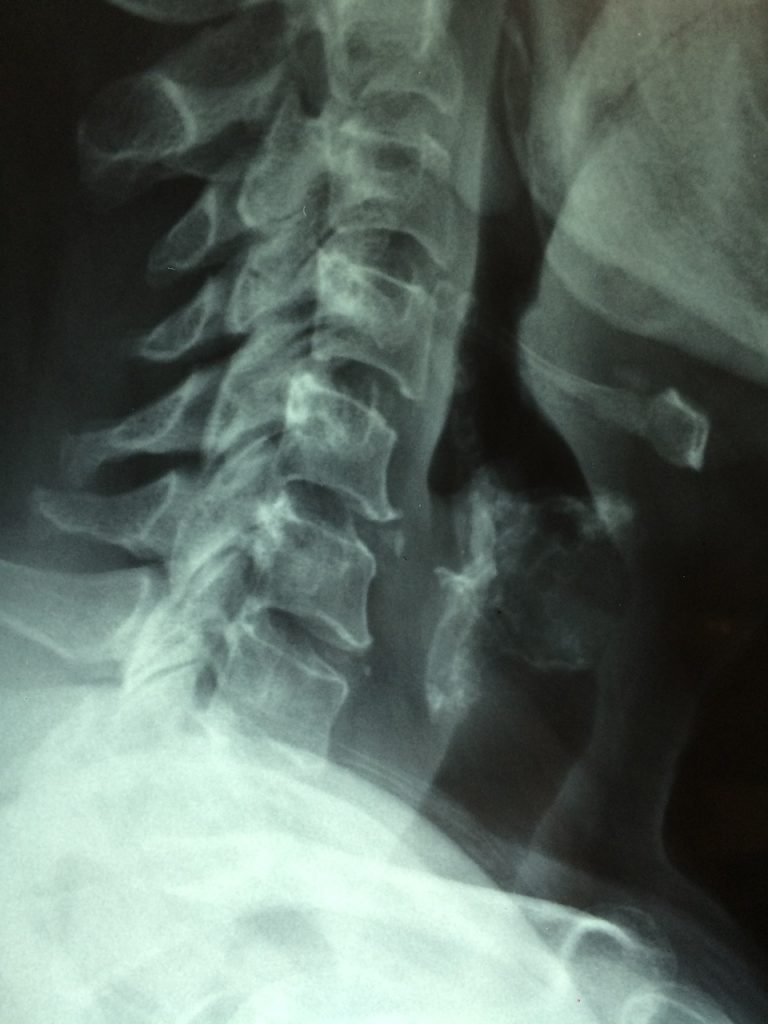
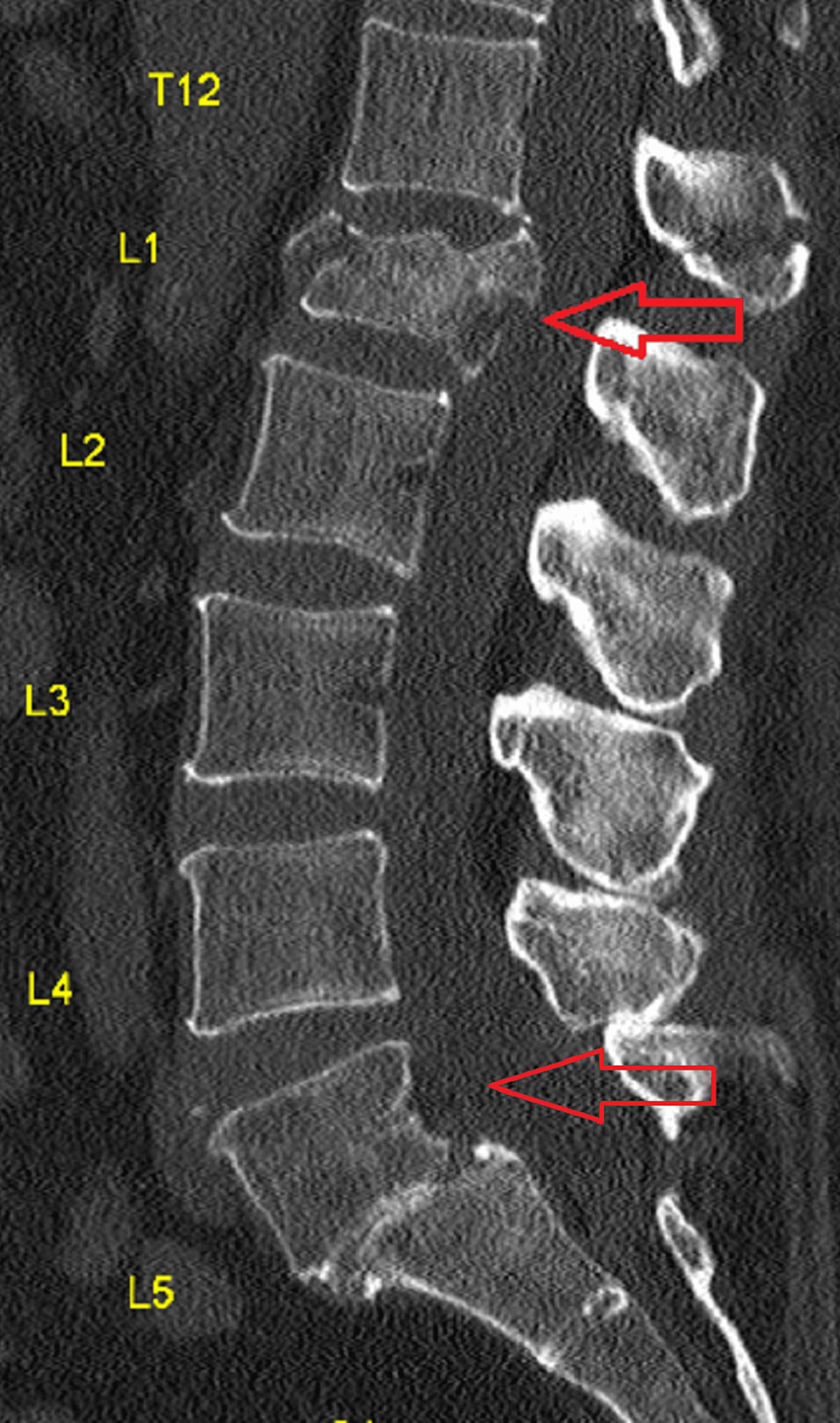
Vertebral fractures commonly occur at the thoracolumbar junction. These fractures can be treated with mild residual deformity in many cases, but are reportedly associated with increased risk of secondary vertebral fractures. In the present study, a three‑dimensional (3D) whole spine model was constructed using the finite element method to explore the mechanism of development of compression fractures. The 3D model of the whole spine, from the cervical spine to the pelvis, was constructed from computed tomography (CT) images of an adult male. Using a normal spine model and spine models with compression fractures at the T11, T12 or L1 vertebrae, the distribution of strain was analyzed in the vertebrae after load application. The normal spine model demonstrated greater strain around the thoracolumbar junction and the middle thoracic spine, while the compression fracture models indicated focused strain at the fracture site and adjacent vertebrae. Increased load time resulted in the extension of the strain region up to the middle thoracic spine. The present findings, that secondary vertebral fractures commonly occur around the fracture site, and may also affect the thoracic vertebrae, are consistent with previous clinical and experimental results. These results suggest that follow‑up examinations of compression fractures at the thoracolumbar junction should include the thoracic spine and adjacent vertebrae. The current data also demonstrate that models created from CT images can be used for various analyses.

PDF) Finite Element Method Analysis of Compression Fractures on Whole-Spine Models Including the Rib Cage

Dynamics of spinal cord compression with different patterns of thoracolumbar burst fractures: Numerical simulations using finite element modelling - ScienceDirect

Sagittal Imbalance may lead to higher risks of Vertebral Compression Fractures and Disc Degeneration – A Finite Element Analysis – Sunset Chiropractic & Wellness – Miami Scoliosis Chiropractors
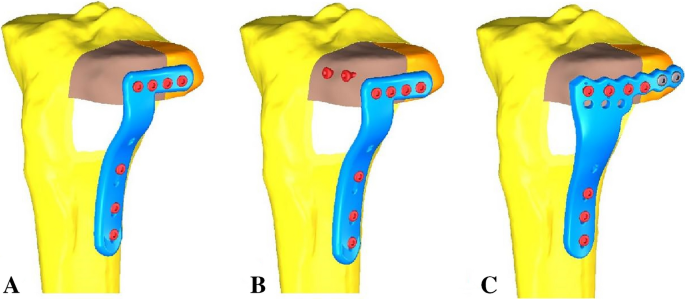
The study of biomechanics and finite element analysis on a novel plate for tibial plateau fractures via anterolateral supra-fibular-head approach

Three-dimensional finite element model to predict patterns of pterygomaxillary dysjunction during Le Fort I osteotomy

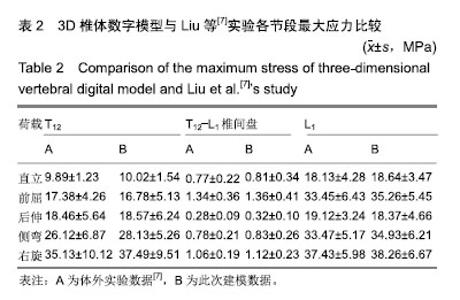
Orthopaedic Modular Implants Based on Shape Memory Alloys
Finite Element Method Analysis of Compression Fractures on Whole-Spine Models Including the Rib Cage - Document - Gale OneFile: Health and Medicine

PDF] Finite Element Method Analysis of Compression Fractures on Whole-Spine Models Including the Rib Cage
Frontiers Biomechanical Evaluation and the Assisted 3D Printed Model in the Patient-Specific Preoperative Planning for Thoracic Spinal Tuberculosis: A Finite Element Analysis
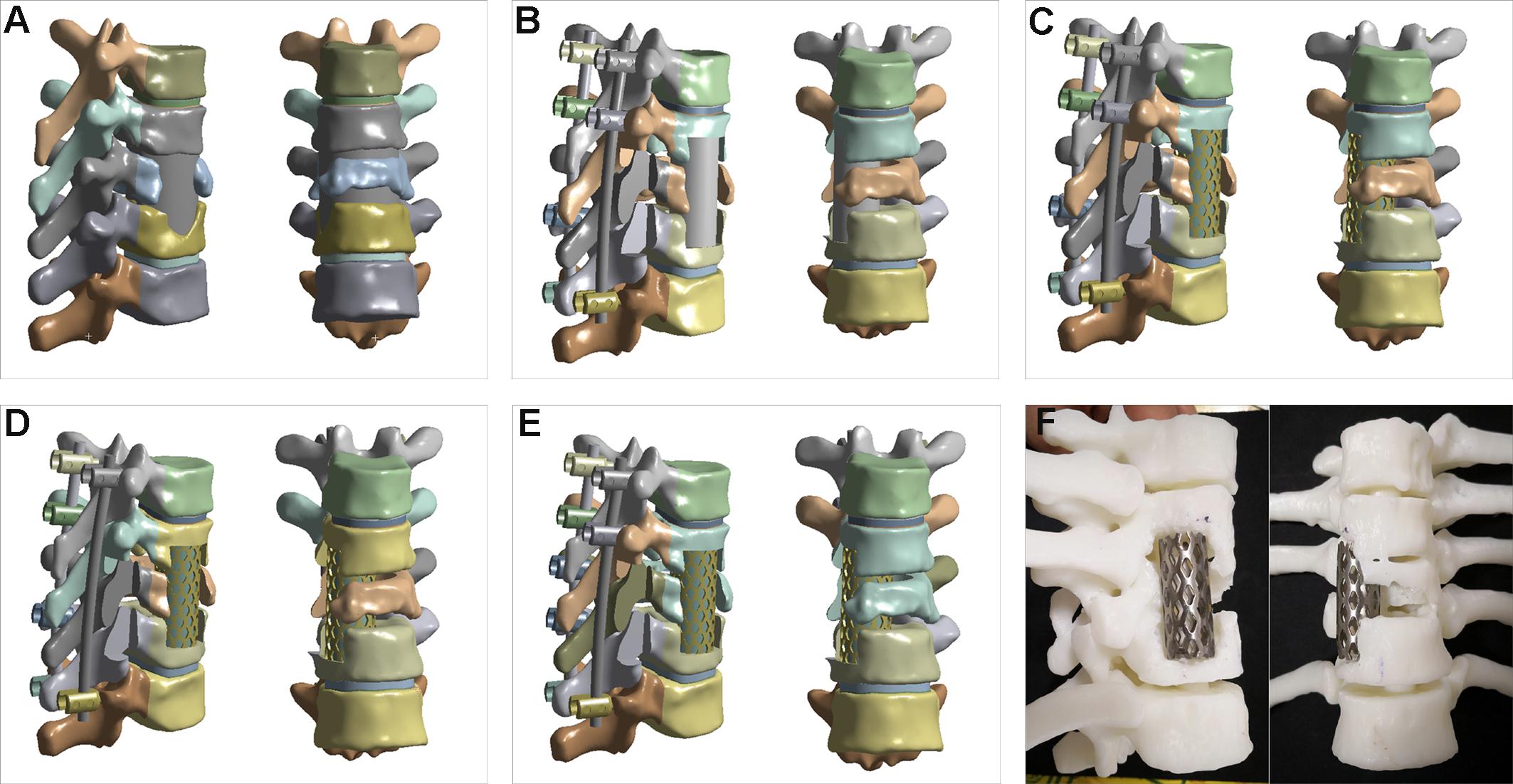
Mechanical changes of percutaneous kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar compressive fractures in three-dimensional vertebral models
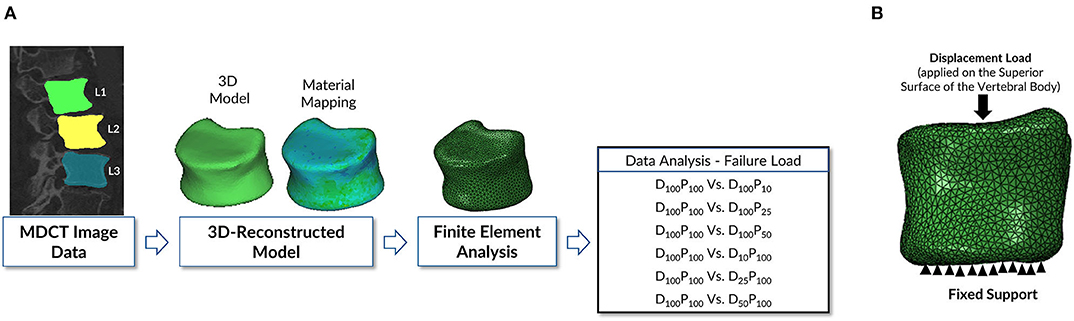
Frontiers Finite Element Analysis-Based Vertebral Bone Strength Prediction Using MDCT Data: How Low Can We Go?

PDF) Finite element analysis of compression fractures at the thoracolumbar junction using models constructed from medical images

Finite Element Analysis of Fracture Fixation
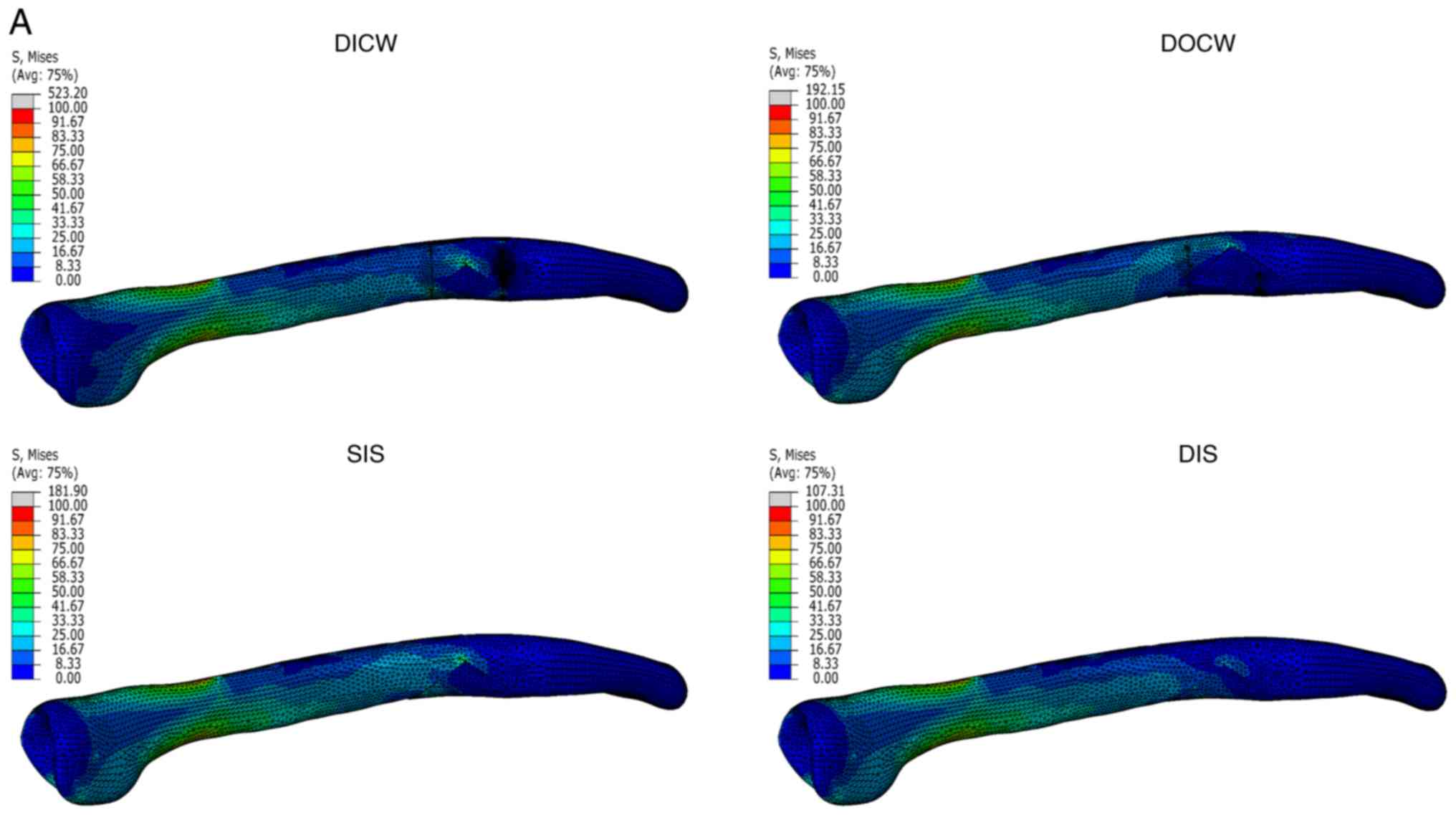
Biomechanical analysis of four augmented fixations of plate osteosynthesis for comminuted mid‑shaft clavicle fracture: A finite element approach

Biomechanical considerations in the design of patient-specific fixation plates for the distal radius