1 Slope Stability Failure Planes or Slip Surfaces Text section 14.9 and only. - ppt download

3 Slope Stability In slope stability analysis we determine the Factor of Safety as a ratio of resisting forces to driving forces F s = Resisting / Driving Theoretically, any slope with a Factor of Safety less than one will fail and any slope with a factor of safety greater than one will not. Design focuses on the soil parameters and geometry that will provide the maximum factor of safety. Sometimes, the analysis of an existing slope will be what is called a parametric study – that is establishing a factor of safety and performing an analysis that back calculates the strength parameters. The engineer will then determine his/her confidence level as to whether or not the soil has that strength through experience, lab, and/or field data.
1 Slope Stability Failure Planes or Slip Surfaces Text section 14.9 and only
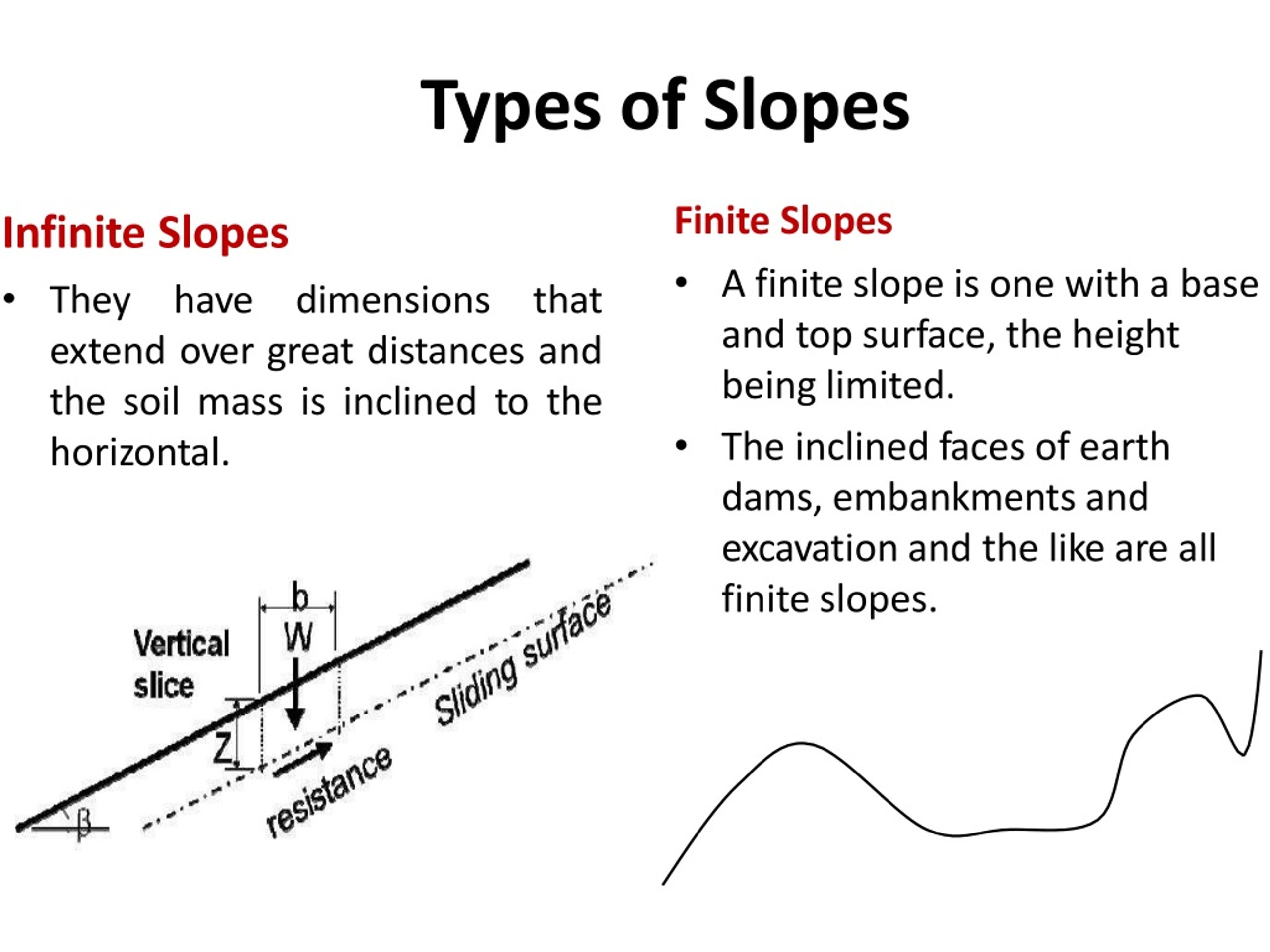
2 Slope Stability In general you have: Driving Force – Weight of Slope Resisting Force – Strength of soil along slip surface Buttress at toe W c
Design focuses on the soil parameters and geometry that will provide the maximum factor of safety. Sometimes, the analysis of an existing slope will be what is called a parametric study – that is establishing a factor of safety and performing an analysis that back calculates the strength parameters. The engineer will then determine his/her confidence level as to whether or not the soil has that strength through experience, lab, and/or field data..
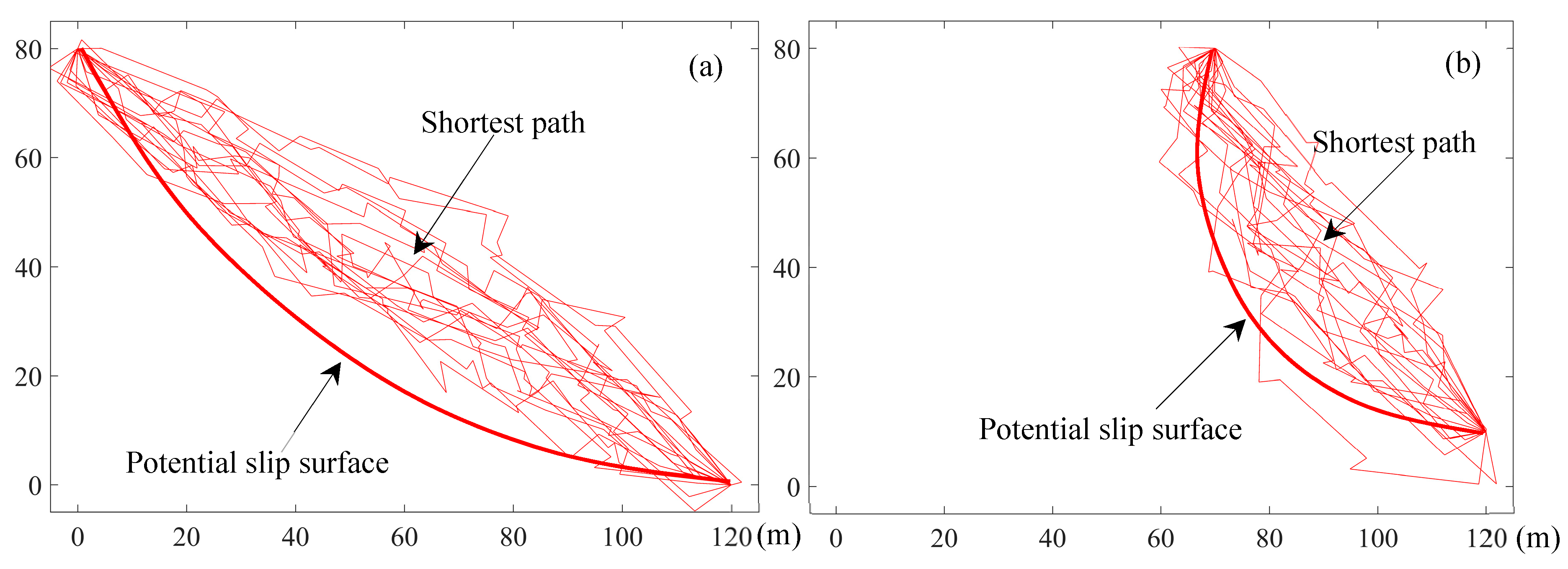
4 Slope Stability Example of Circular Slip Surface (from geoslope software) Circular slip surfaces often used in analysis as the most likely approximated shape of the failure surface
5 Slope Stability Non circular slip surfaces can also be analyzed
Now: W n sin α (driving) N= W n cos α T r = shear face = c’ + F ’ tan φ’ (resisting) W n sinα W n cos α α.
7 Slope Stability Performing this analysis on each slice and then summing the components from each slice F s = Σ (c L + W cos α tan φ) / Σ (W sin α )
8 Slope Stability This analysis is very conducive to a tabular solution WedgecφαLWW sin αc LW cos α tanφ8 + 9 F s = Σ (10) / Σ (7)
9 Slope Stability - Example Each box is 5’ x 5’ * = 120 pcf c = 300 psf φ = 32 o
10 Slope Stability - Example First, Find the areas for each slice A1 A2 A3 A4
11 Slope Stability WedgecφαLWW sin αc LW cos α tanφ F s = Σ (10) / Σ (7)

Hydrogeologic characterization of Area B, Fort Detrick, Maryland

A practical procedure for the back analysis of slope failures in closely jointed rock masses - ScienceDirect

A practical procedure for the back analysis of slope failures in closely jointed rock masses - ScienceDirect

Blog — McLindon Geosciences, LLC

Facile and Scalable Fabrication of High-Performance Polylactide-Based Medical Microparts through Combining the Microinjection Molding Intense Shear Stress Field and Annealing Strategy

Download full text - ELSA - Europa
PPT - Slope Stability PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:277684

images./33/8194036/slides/slide_5.j

Large-Eddy Simulation of a Katabatic Jet along a Convexly Curved Slope. Part I: Statistical Results in: Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences Volume 74 Issue 12 (2017)

Influence of Interfacial Bonding on the Mechanical and Impact Properties Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymer (ROMP) Silica Composites

1 Slope Stability Failure Planes or Slip Surfaces Text section
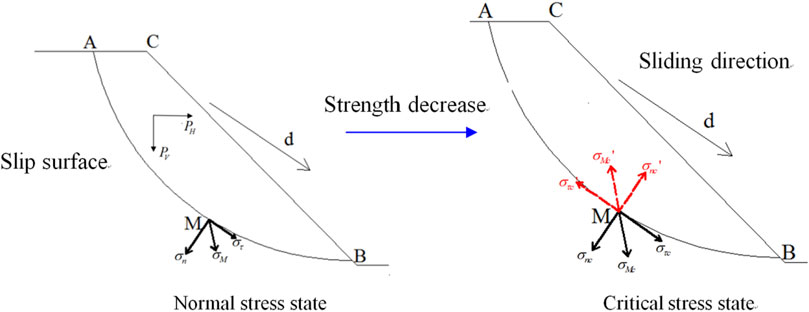
Frontiers Determining the Critical Slip Surface of Slope by Vector Sum Method Based on Strength Reduction Definition

NHESS - Probabilistic landslide susceptibility analysis in tropical mountainous terrain using the physically based r.slope.stability model