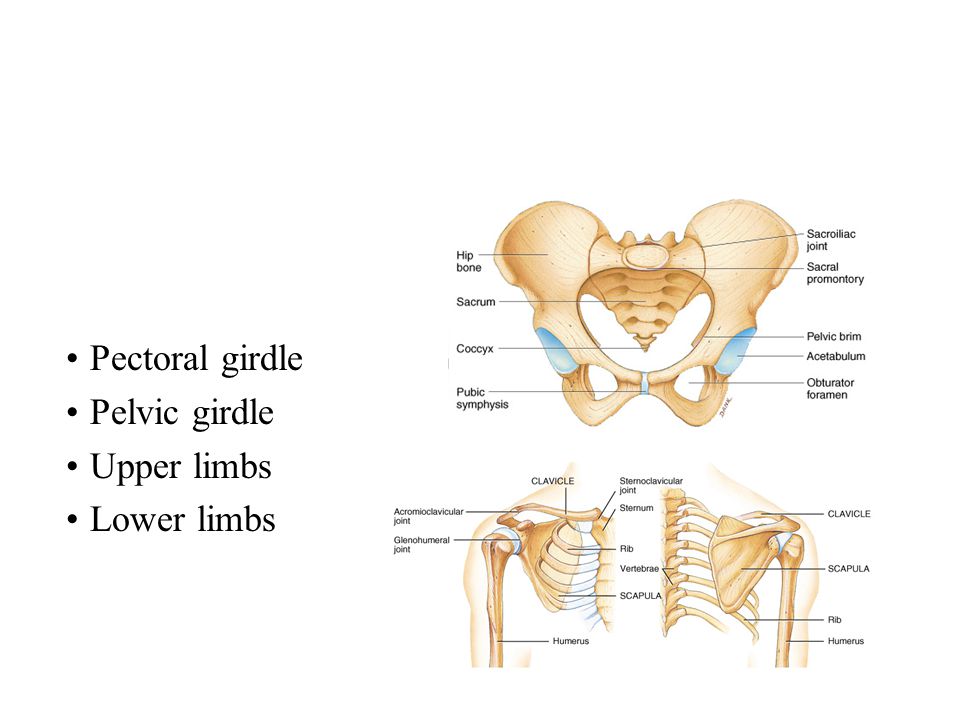
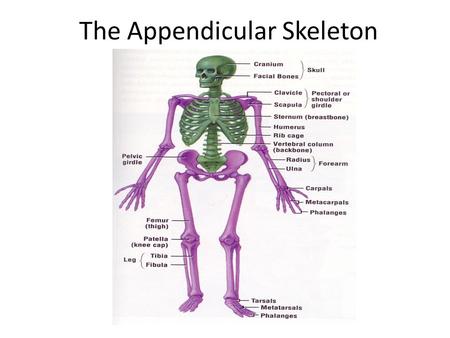
Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs. - ppt video online download
Upper Extremity Clavicle Scapula Humerus Radius and Ulna Carpals, Metacarpals Phalanges
Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs.
Carpals, Metacarpals. Phalanges.
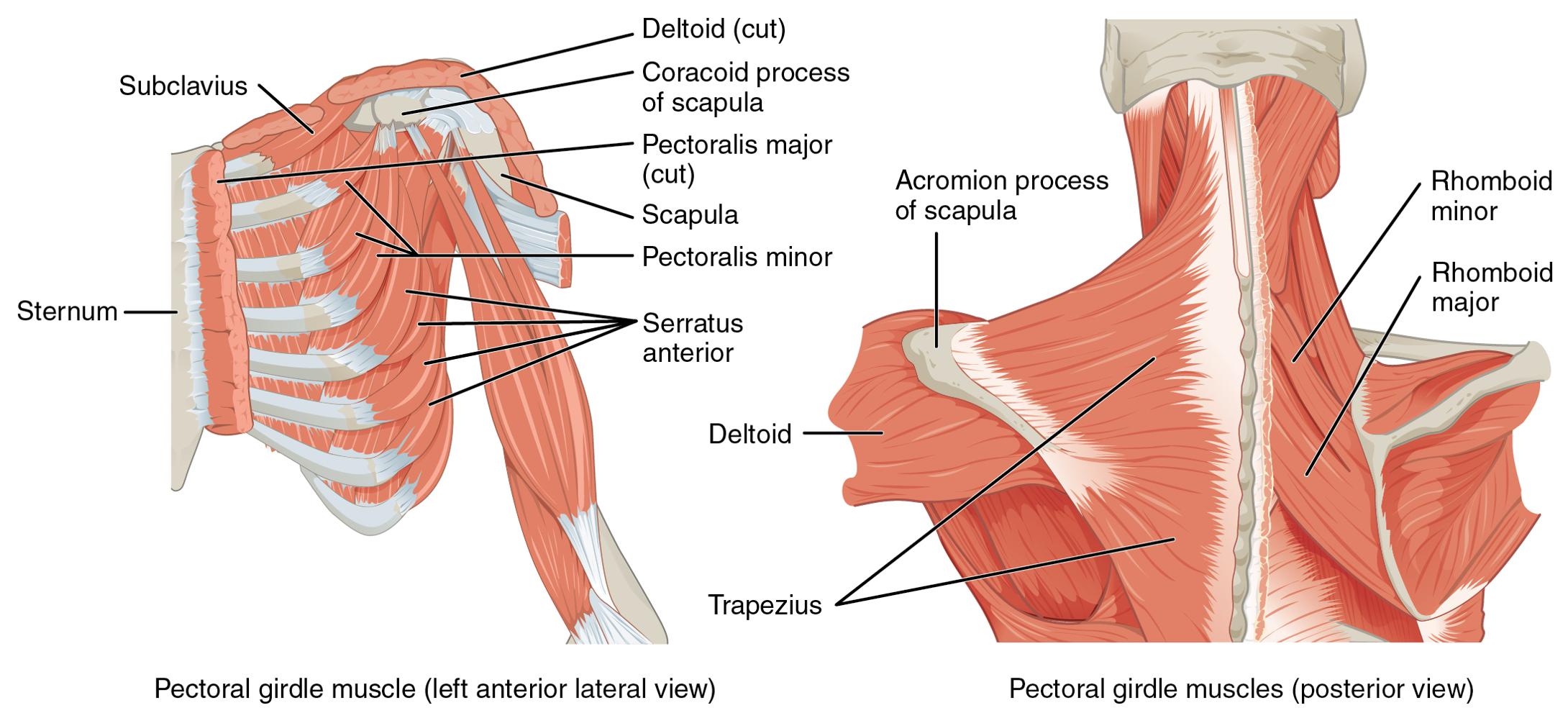
Consists of scapula and clavicle. Clavicle articulates with sternum (sternoclavicular joint) Clavicle articulates with scapula (acromioclavicular joint) Scapula held in place by muscle only. Upper limb attached to pectoral girdle at shoulder (glenohumeral joint)
S-shaped bone with two curves. medial curve convex anteriorly/lateral one concave anteriorly. Extends from sternum to scapula above 1st rib. Fracture site is junction of curves. Ligaments attached to clavicle stabilize its position.
Sternal extremity: end that articulates with the sternum. Acromional extremity: end that articulates with the scapula. Body: center portion of clavicle.
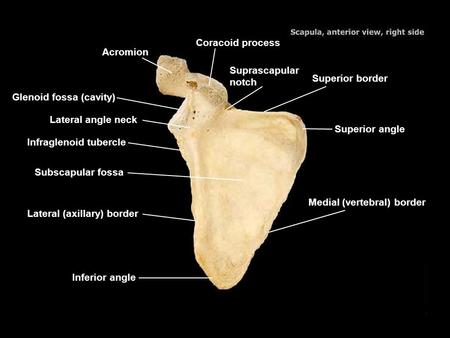
Triangular flat bone found in upper back region. Scapular spine ends as acromion process. a sharp ridge widening to a flat process. Glenoid cavity forms shoulder joint with head of humerus. Supraspinous & infraspinous fossa for muscular attachments.
Superior Border: Upper margin. Vertebral Border: Margin toward vertebral column. Axillary Border: Lateral margin ( towards the humerus ) Spine: Sharp ridge running diagonally across posterior surface of shoulder blade. Acromion process: Slightly flaring projection at lateral end of scapular spine; may be felt as tip of shoulder; articulates with clavicle. Coracoid process: Projection on anterior surface from upper border of bone; may be felt in groove between deltoid and pectoralis major muscle.
Subscapular fossa filled with muscle. Coracoid process for muscle attachment.
Infraspinous Fossa: Surface area below the spine on the Dorsal surface. Supraspinous Fossa: surface area above the spine on the dorsal surface. Supraglenoid tubercle: process above the glenoid cavity.
Superior angle: angle formed between the superior border and the vertebral border. Inferior angle: angle formed between the axillary and vertebral borders.
humerus within the arm. ulna & radius within the forearm. carpal bones within the wrist. metacarpal bones within the palm. phalanges in the fingers. Joints. shoulder (glenohumeral), elbow, wrist, metacarpophalangeal, interphalangeal.
Greater tubercle: Rounded projection lateral to head on anterior surface. Lesser tubercle: Prominent projection on anterior surface just below anatomical neck.
Deltoid tuberosity: V-shaped, rough area about midway down the shaft where Deltoid muscle inserts.
Part of shoulder joint. Head & anatomical neck. Greater & lesser tubercles for muscle attachments. Intertubercular sulcus or bicipital groove. Surgical neck is fracture site. Deltoid tuberosity. Shaft.
Medial Epicondyle: rough projection on the medial side of distal end of humerus. Capitulum: Rounded knob below lateral epicondyle: articulates with head of Radius. Trochlea: Projection on distal end of humerus with a deep depression through the center, resembles a pulley.
Coronoid Fossa: Depression on anterior surface above Trochlea receives coronoid process of ulna in flexion of lower arm.
Capitulum. articulates with head of radius. Trochlea. articulation with ulna. Olecranon fossa. posterior depression for olecranon process of ulna. Medial & lateral epicondyles. attachment of forearm muscles.
Head of Radius: Disk shaped process forming proximal end of radius articulates with capitulum of humerus and radial notch of ulna. Radial tuberosity: Roughened projection on ulna side, short distance below head. Neck of Radius: constricted portion below the head.
Radius cont. Styloid Process of Radius: Protuberance at distal end on lateral surface.
Ulna (on little finger side) trochlear notch articulates with humerus & radial notch with radius. olecranon process forms point of elbow. Radius (on thumb side) head articulates with capitulum of humerus & radial notch of ulna. tuberosity for muscle attachment.
Olecranon Process: Elbow. Semilunar Notch: curved notch between olecranon process and coronoid process into which the trochlea fits. Coronoid Process: Projection on anterior surface of proximal end of ulna. Radial Notch: curved notch lateral and inferior to semilunar notch: head of radius fits into this cavity.
Styloid Process of ulna: Sharp protuberance at distal end, can be seen from outside on posterior surface.
Ulna articulates with trochlea of humerus. Radius articulates with capitulum of humerus. Interosseous membrane between ulna & radius provides site for muscle attachment.
Ulna --styloid process. head separated from wrist joint by fibrocartilage disc. Radius. forms wrist joint with scaphoid, lunate & triquetrum. forms distal radioulnar joint with head of ulna.
scaphoid - boat shaped. lunate - moon shaped. triquetrum - 3 corners. pisiform - pea shaped. Distal row - lateral to medial. trapezium - four sided. trapezoid - four sided. capitate - large head. hamate - hooked process. Carpal tunnel--tunnel of bone & flexor retinaculum.
Distal Row: hamate, capitate, trapezoid, & trapezium.
Numbered from Thumb to little finger. I, II, III, IV, V.
Fingers: Proximal, Middle, & Distal Phalanx. Thumb: Proximal & Distal Phalanx only.
5 total----#1 proximal to thumb. base, shaft, head. knuckles (metacarpophalangeal joints) Phalanges. 14 total: each is called phalanx. proximal, middle, distal on each finger, except thumb.
Lower Extremities. Pelvis. Femur. Tibia,Fibula. Tarsals, Metatarsals. Phalanges.
Pelvic girdle = two hipbones united at pubic symphysis. articulate posteriorly with sacrum at sacroiliac joints. Each hip bone = ilium, pubis, and ischium. fuse after birth at acetabulum. Bony pelvis = 2 hip bones, sacrum and coccyx.
lesser sciatic notch. ramus. Pubis. body. superior & inferior ramus. pubic symphysis is pad of fibrocartilage between 2 pubic bones.
Ischium: Lower, posterior portion. Pubic bone (pubis): Medial, anterior section. Acetabulum: Hip socket; formed by union of ilium, ischium, and pubis. Iliac Crest: upper, curving boundary of ilium.
A. Anterior superior: Prominent projection at anterior end of iliac crest; can be flelt externally as point of hip. B. Anterior inferior: Less prominent projection short distance below anterior superior spine.
D. Posterior inferior: Just below posterior superior spine. Greater Sciatic Notch: Large notch on posterior surface of ilium just below posterior inferior spine.
Obtuator foramen: large hole in anterior surface of os coxa; formed by pubis and ischium; largest foramen in body. Ischial Tuberosity: Large rough, quadrilaterial process forming inferior part of ischium.
Superior Ramus of Pubis: Part of pubis lying between symphysis and acetabulum; forms upper part of obturator foramen. Inferior Ramus of Pubis: Part extending dowwn from symphysis unites with ischium. Pubis: lower part of pelvis.
Iliac fossa for muscle attachment. Gluteal lines indicating muscle attachment. Sacroiliac joint at auricular surface & iliac tuberosity. Greater sciatic notch for sciatic nerve.
Pubic crest: Upper margin of superior ramus.
sacral promontory to symphysis pubis. separates false from true pelvis. false pelvis holds only abdominal organs. Inlet & outlet. Pelvic axis = path of babies head.
larger and heavier. larger articular surfaces. larger muscle attachments. Female pelvis. wider & shallower. larger pelvic inlet & outlet. more space in true pelvis. pubic arch >90 degrees.
femur and patella within the thigh. tibia & fibula within the leg. tarsal bones in the foot. metatarsals within the forefoot. phalanges in the toes. Joints. hip, knee, ankle. proximal & distal tibiofibular. metatarsophalangeal.
longest & strongest bone in body. head articulates with acetabulum (attached by ligament of head of femur) neck is common fracture site. greater & lesser trochanters, linea aspera, & gluteal tuberosity-- muscle attachments. medial & lateral condyles articulate with tibia. patellar surface anteriorly between condyles. Patella. triangular sesamoid. increases leverage of quadriceps femoris tendon.
Head: rounded upper end of bone; fits into acetabulum. Neck: Constricted portion just below head. Greater Trochanter: Protuberance located inferiorly and laterally to head. Lesser Trochanter: Small protuberance located inferiorly and medially to greater.
Condyles: Large, rounded bulges at distal end of femur, one medial and one lateral. Epicondyles: Blunt projections from the sides of the condyles; one on the medial aspect and on the lateral aspect. Adductor tubercle: Small projection just above medial condyle; marks termination of medial supracondylar ridge.
Intercondyloid fossa: Deep depression between condyles on posterior surface; cruciate ligaments that help bind femur to tibia lodge in this notch.
Patella Kneecap; largest sesamoid bone of the body; embedded in tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle.
weight-bearing bone. lateral & medial condyles. tibial tuberosity for patellar lig. proximal tibiofibular joint. medial malleolus at ankle. Fibula. not part of knee joint. muscle attachment only. lateral malleolus at ankle.
Intercondylar eminence: Upward projection on articular surface between condyles. Crest: Sharp ridge on anterior surface. Tibial tuberosity: Projection in midline on anterior surface.
Medial malleolus: Rounded downward projection at distal end of tibia; forms prominence on medial surface of ankle.
Lateral malleolus: Rounded prominence at distal end of fibula; forms proninence on lateral surface of ankle. Head: Prominence on proximal end of Fibula; articulates with lateral surface of tibia. This is the non weight bearing bone of the lower leg.
Talus = ankle bone (articulates with tibia & fibula) Calcaneus - heel bone. Cuboid, navicular & 3 cuneiforms.
Calcaneus: heel bone. Talus: Uppermost of tarsals; articulates with tibia and fibula; boxed in by medial and lateral malleolus. Navicular: articulates with the talus and cuneiforms I, II, & III.
Cuboid: forms side of ankle; articulates with calcaneus and IV & V Metatarsals.
midregion of the foot. 5 metatarsals (1 is most medial) each with base, shaft and head. Phalanges. distal portion of the foot. similar in number and arrangement to the hand. big toe is hallux.
Numbered like the metacarpals of the hand. I - big toe through V - little toe.
Phalanges Miniature long bones of the toes; two in each great toe; three in other toes.
distribute body weight over foot. yield & spring back when weight is lifted. Longitudinal arches along each side of foot. Transverse arch across midfoot region. navicular, cuneiforms & bases of metatarsals.
weakened ligaments allow bones of medial arch to drop. Clawfoot. medial arch is too elevated. Hip fracture. 1/2 million/year in US. osteoporosis. arthroplasty.

/slide/4225255/14/images/3/Pectoral

/slide/4225255/14/images/2/Upper+Ex

/14/4225175/big_thumb.jpg
/14/4225108/big_thumb.jpg
/14/4199555/big_thumb.jpg

/4225255/14/images/slide_1.jpg
/14/4189002/big_thumb.jpg